¶ The Selection of OIDC Authorization Mode
You need to choose an appropriate authorization mode according to your scenario and the type of application you are developing. This article will assist you in choosing the appropriate OIDC authorization mode.
¶ Recommended Authorization Mode
Different types of applications require different authorization modes. The following table is our recommended mode:
| Application Type | Authorization Mode |
|---|---|
| With backend | Authorization Code Mode |
| SPA, no backend | Implicit Mode |
| Between servers | Client Credentials |
¶ Does Your Application Need Id Token?
| Authorization Mode | Access Token | Id Token |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization Code Mode | ✅ | ✅ |
| Implicit Mode | ✅ | ✅ |
| Password Mode | ✅ | ✅ |
| Client Credentials Mode | ✅ | ❌ |
¶ What Type of Your Application is?
How to choose the OIDC authorization model depends on which type of application you are developing. Refer to the following flowchart to select the authorization mode you need:

¶ Is Your Application Code can be Publicly Access?
If your end users can see and modify your application code, then the application is publicly accessible. In this scenario, the application cannot store the key securely, including SPA (Single Page Application) and mobile applications.
¶ Is Your Application a SPA or a Native Application?
If your application is a single page application, running in a new version of the browser, and the browser supports Web Crypto, you should use the PKCE + Authorization Code Mode. If your application is running in an old version of the browser, the browser does not support Web Crypto, you should use the Implicit Mode. The Implicit Mode is only suitable for scenarios where the application cannot safely store the key. If other modes are not available, you should consider using the Implicit Mode.
If your application is a native application, you should use PKCE + Authorization Code Mode.
¶ Are There End Users Using Your App?
If your application runs on the server side and is not directly used by end users, but only for interaction between servers, you should use Client Credentials Mode.
¶ Are Applications And Resources Held by the Same Party?
If your application and the resources that the application needs to access are all controlled by you, and your application can safely store user accounts and passwords with enough safe code logic. When the other authorization modes are not suitable, you can choose the Password Mode.
¶ Authorization Code Mode
The Authorization Code Mode is suitable for scenarios where the application has a backend server. The Authorization Code Mode requires that the application must be able to store the key securely for subsequent use of the authorization code to exchange the Access Token. The Authorization Code Mode requires interaction between the browser and the terminal user to complete authentication and authorization, and then the authorization code is sent to the back-end service through browser redirection, and then the authorization code is exchanged for Token and Token is exchanged for user information.
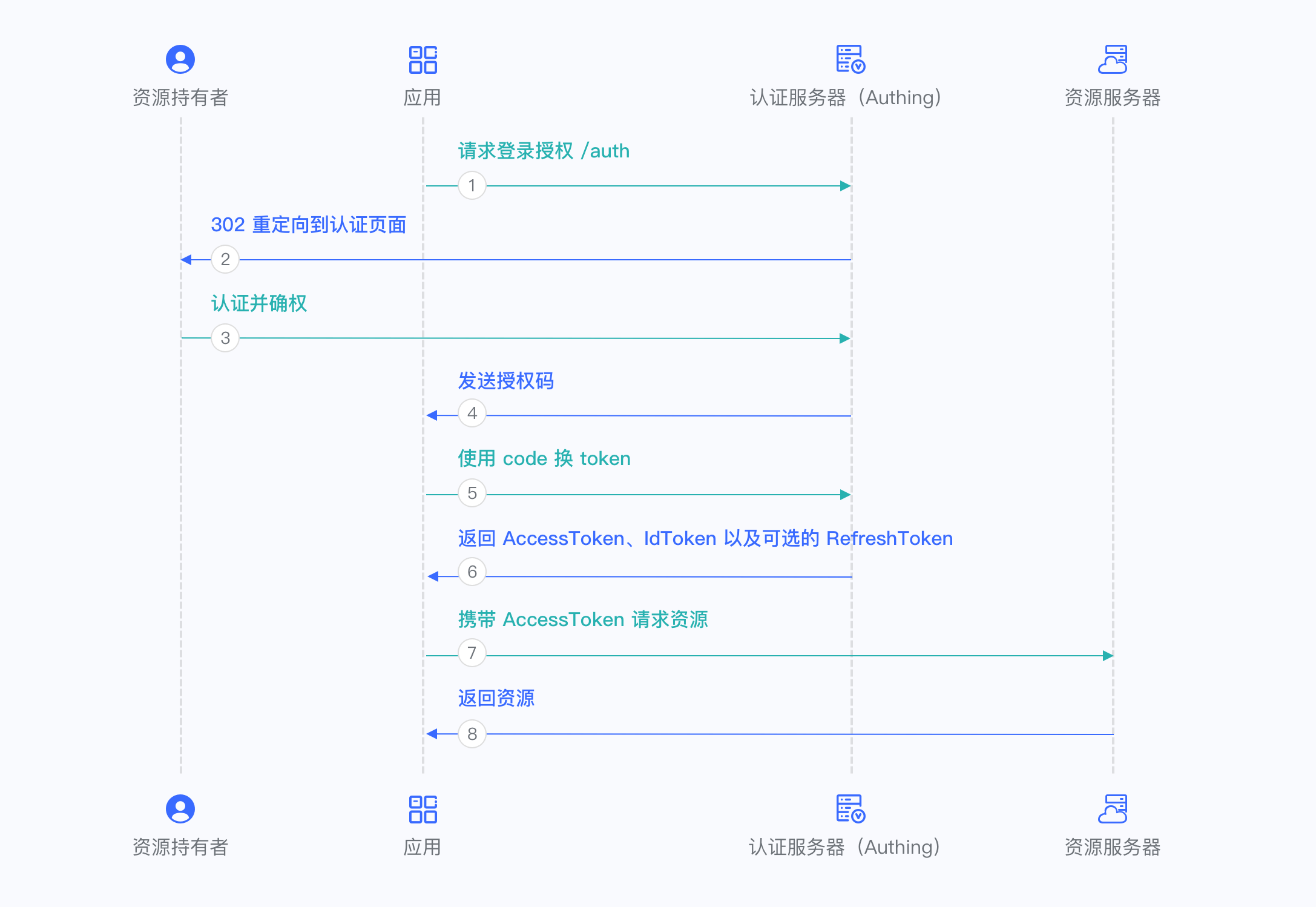
For more information, please refer to Using Authorization Code Mode.
¶ Implicit Mode
The Implicit Mode is suitable for scenarios where the key cannot be stored safely (such as front-end browsers). In the Implicit Mode, the application does not need to use code to exchange tokens, and does not need to request the /token endpoint. AccessToken and IdToken will be returned directly from the authentication endpoint.
Because the Implicit Mode is used in scenarios where the key cannot be stored safely, the Implicit Mode does not support obtaining Refresh Token.
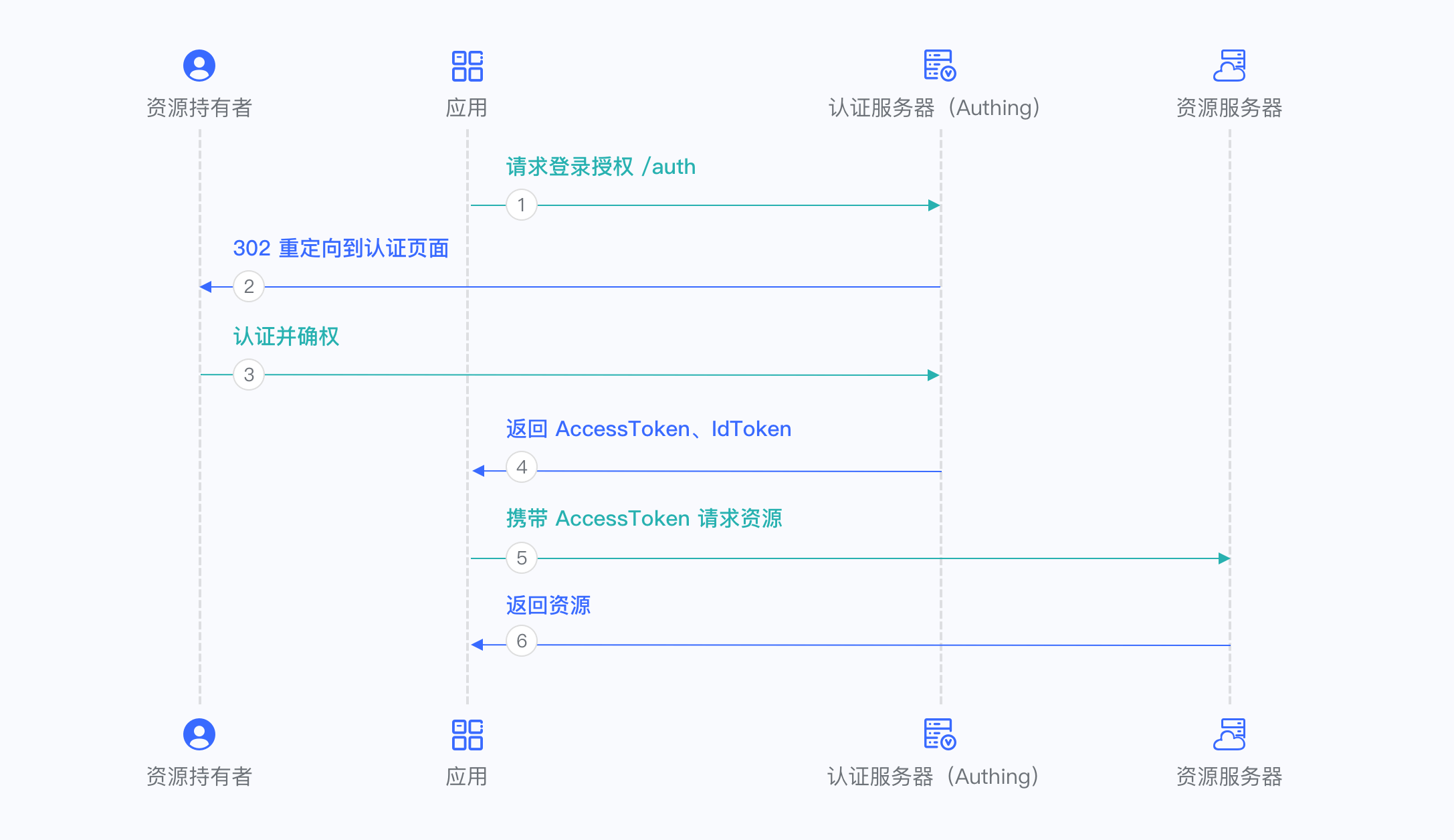
For more information, please refer to Using Implicit Mode.
¶ Password Mode
The Password Mode is suitable for scenarios where you master both the application and the resources required by the application. The Password Mode requires the application to be able to store keys securely and to be able to trustfully store the account secrets of the resource owner. It is generally common for your own apps to use your own resources. The Password Mode does not require redirection, but only needs to carry the user account and secret to access the Token endpoint.
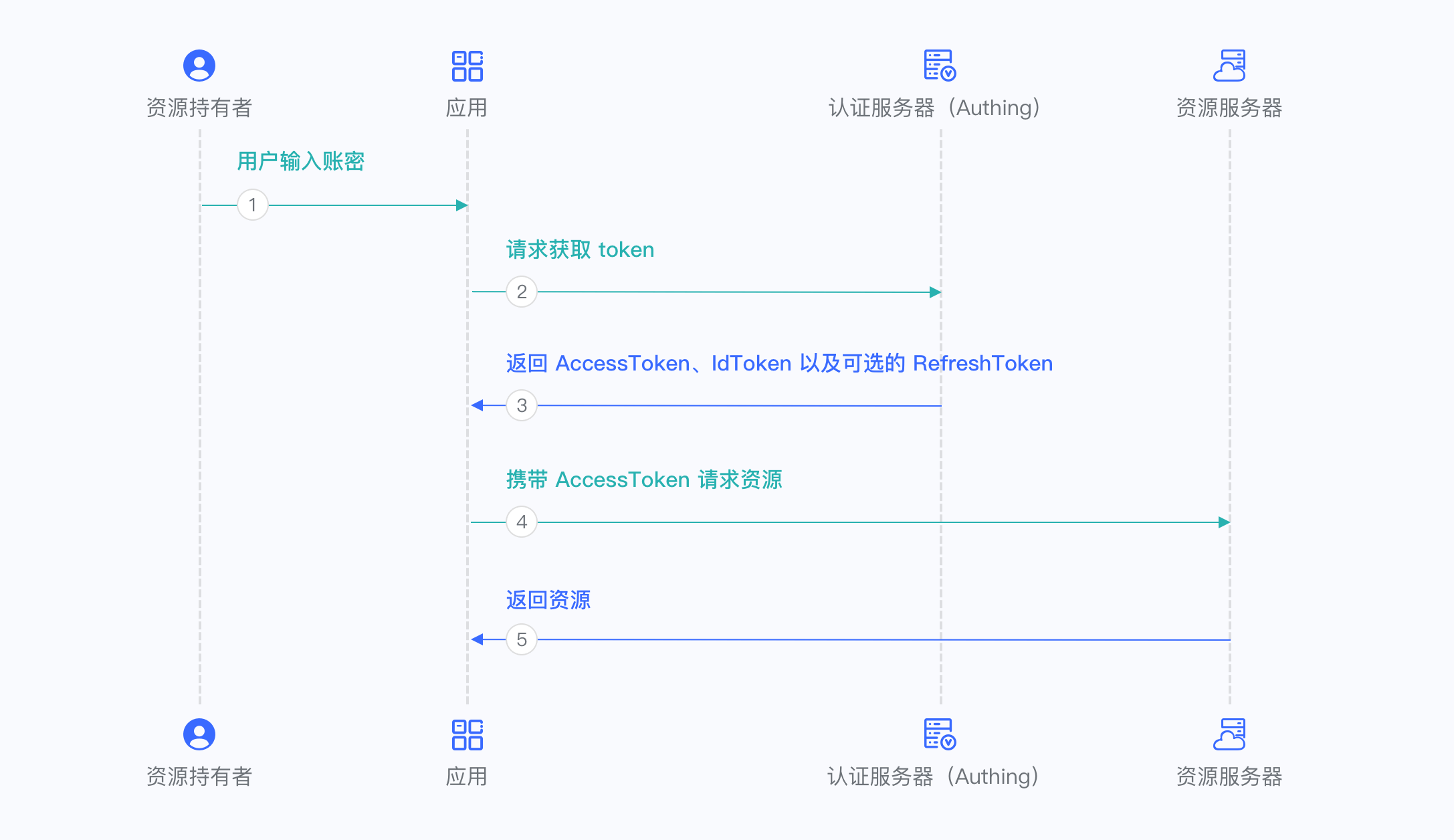
For more information, please refer to Using Password Mode.
¶ Client Credentials Mode
The Client Credentials Mode is used for server-to-server authorization (M2M authorization), during which there is no user involvement. You need to create a programmatic access account and give the AK and SK key pair to your resource caller.
Client Credentials Mode does not support Refresh Token.

For more information, please refer to Use Client Credentials Mode