¶ Manage Resource Privileges
As an administrator, you canmanage and assign resource privileges on the console. Before practicing privilege management and authorization, you need to understand several concepts.
- Application:As an administrator, you can create an application. The application is a definition of the application project you are developing in Authing. For example, when you are actually developing a "web note" application, you should create a "web note" in Authing application.
- Resources:You can define some resources in Authing. For example, the resources in the "Web Notes" application may include notebooks, note content, authors, and so on.
- User:You can also directly assign privileges to users. You can also divide your users into different groups, roles, and organizations, so that you can manage them when assigning privileges.
- Role:A role is a group of users, and the users in the role will automatically inherit the authorized privileges of the role.
Next, we create applications, create resources, create users, and then define the authorization relationship between resources and users.
¶ Create application
Please see the Create application。
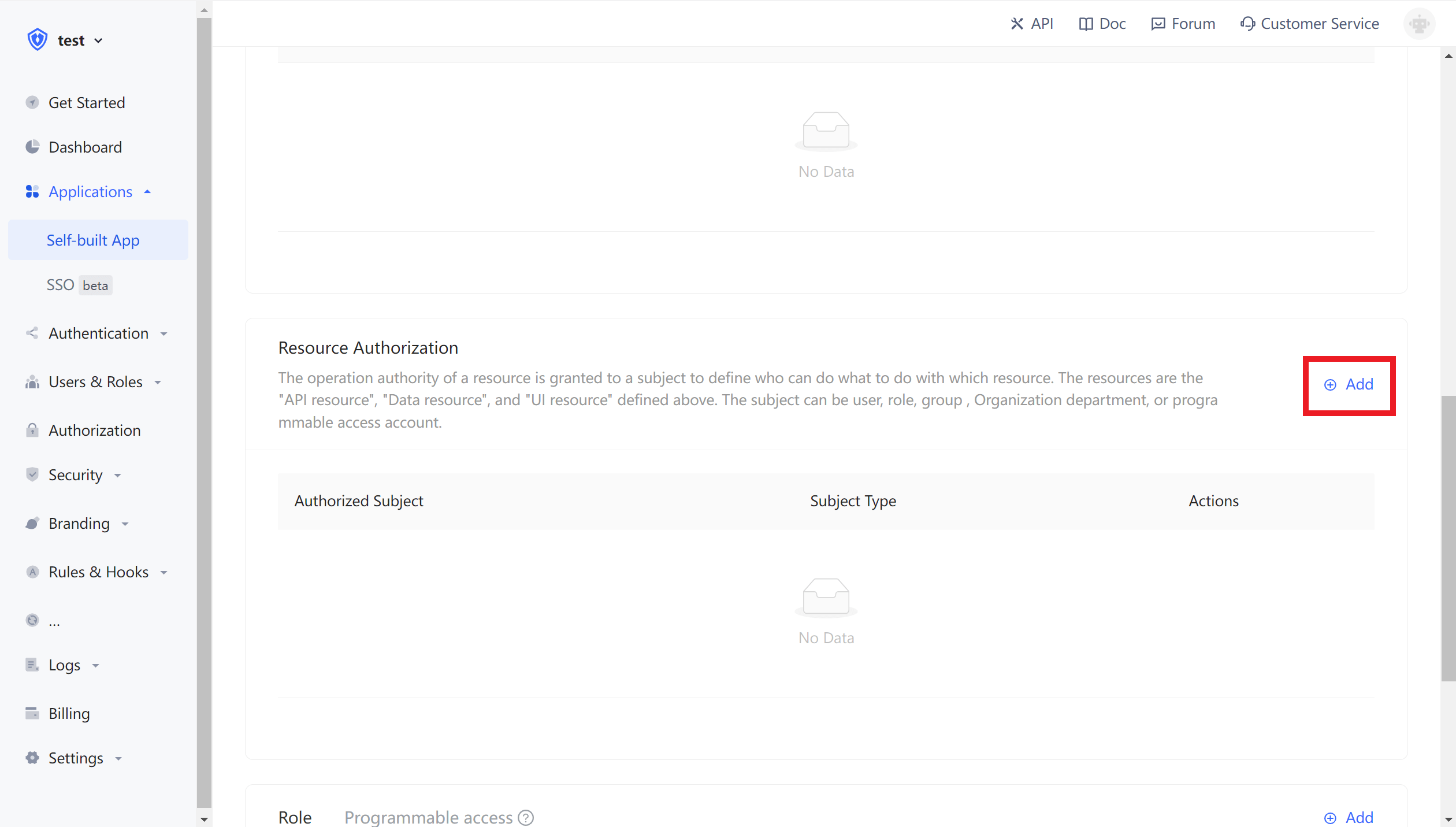
¶ Add Resources
In the resource card under the application, click the Add button on the right.
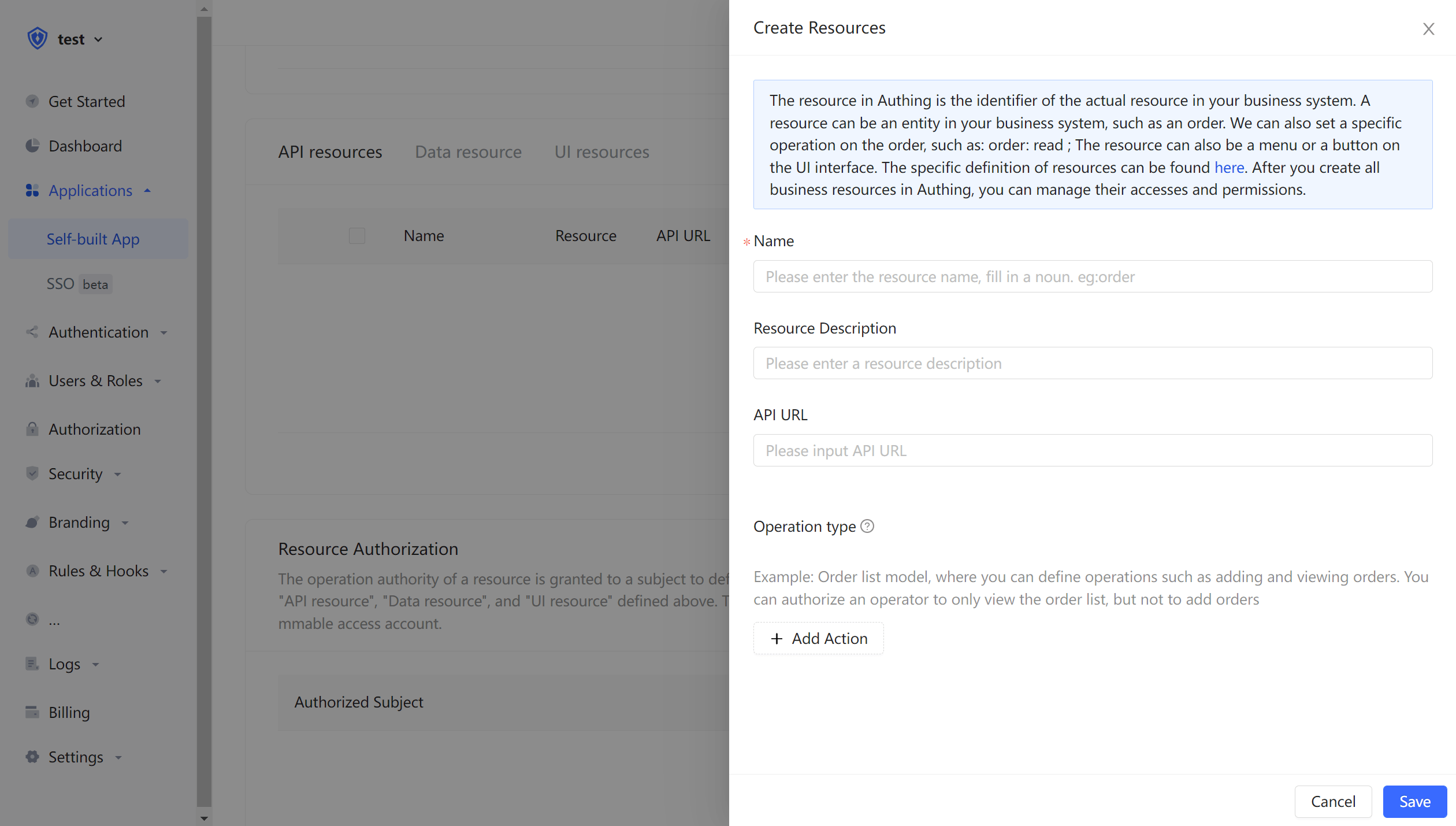
Then fill in a resource name, it is recommended to fill in a semantic resource name to facilitate subsequent management. Resource operations can be defined in the operation type, where read and write operations are defined. Finally, click Save, and a resource is created.
¶ Create a user
In the user list, click New to create a user.
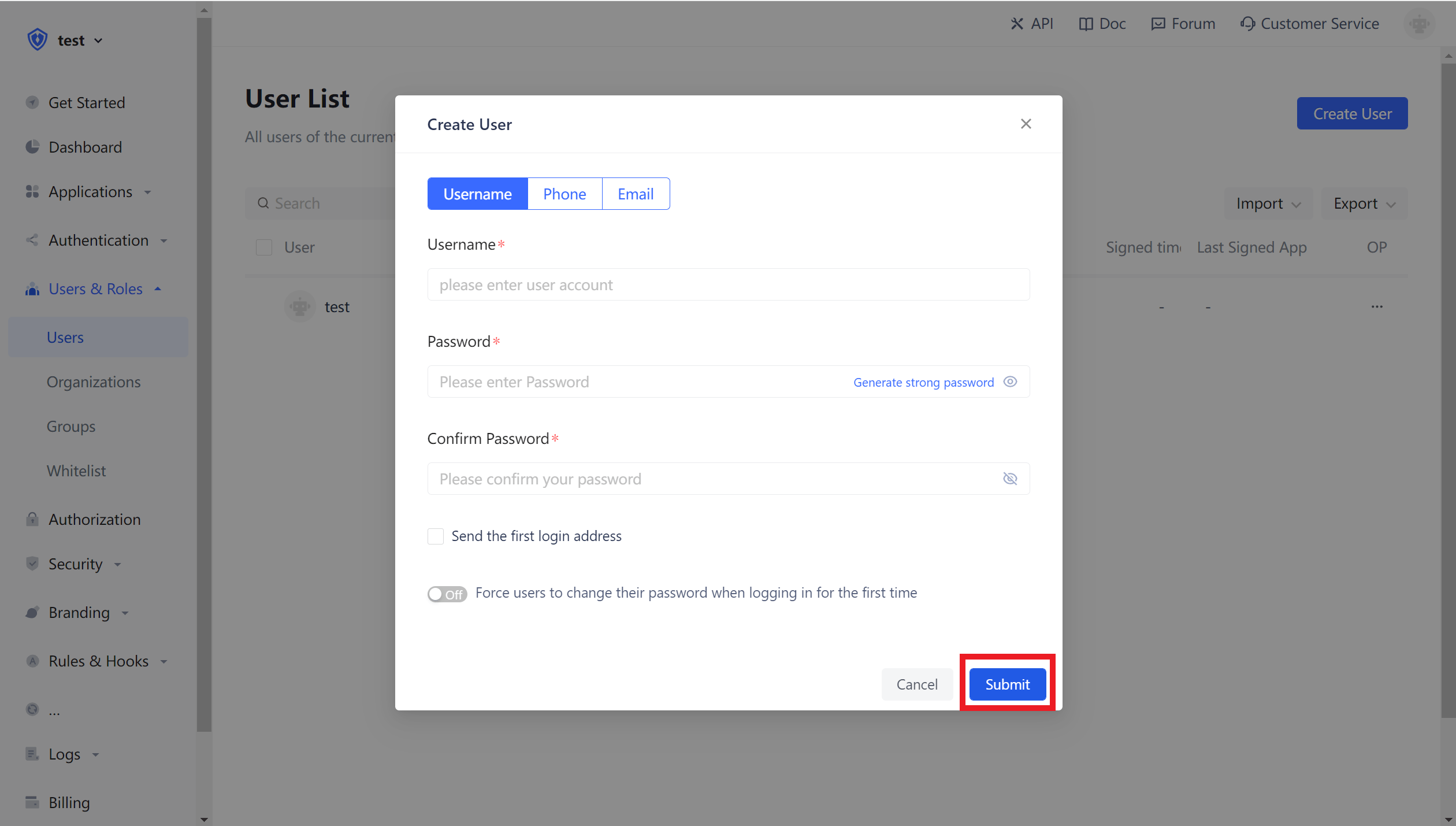
¶ Create a role
In - ApplicationAuthorizationRole Managementcard, click the add button on the right:
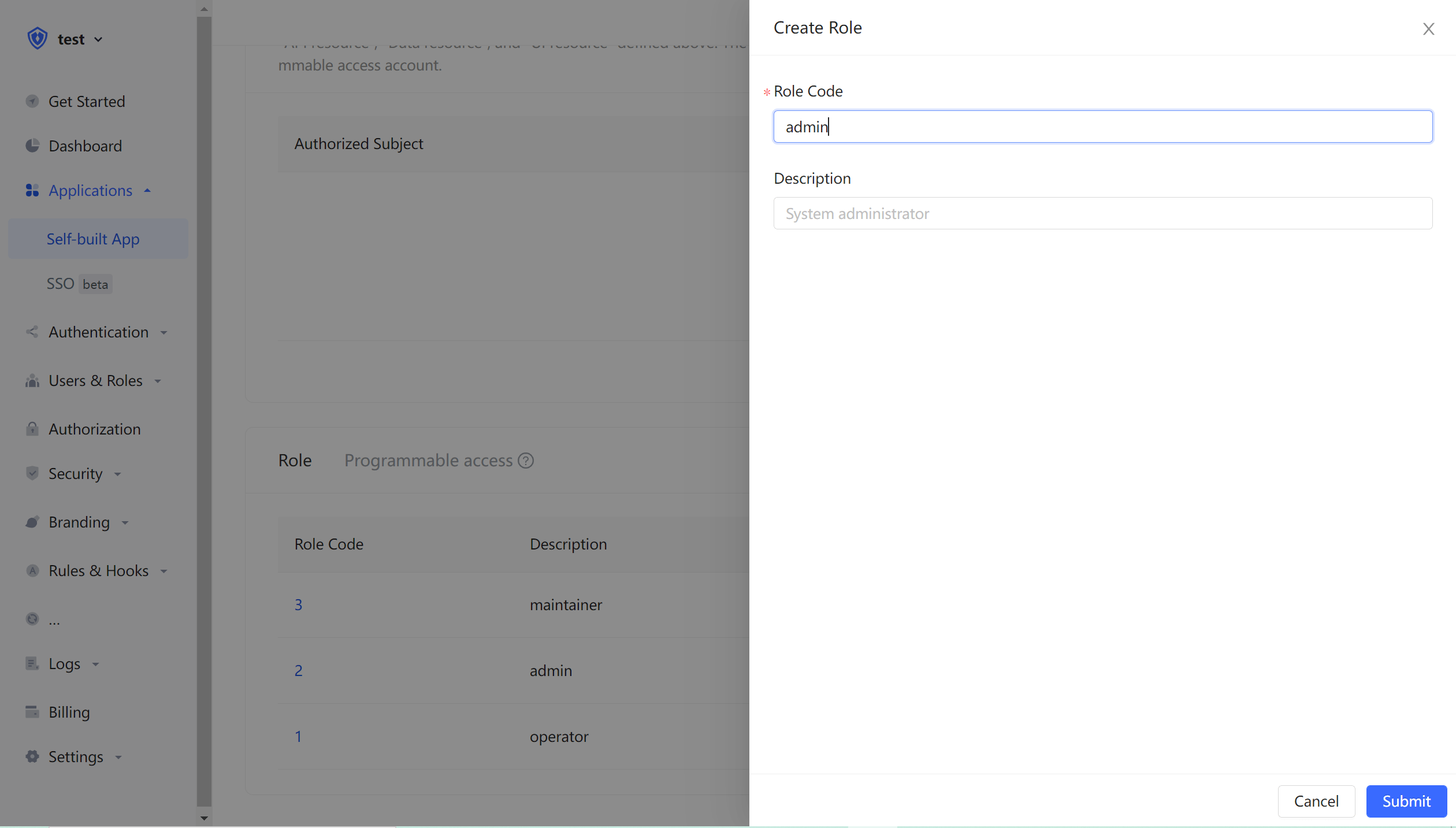
After creating the role, you can add users to this role:
You can search users by username, email or nickname.
¶ Privilege management
Now that you haveresources and users, next you have to define 「who」can do what「operations」on which「resources」In the application’s resource authorization card, click the Add button on the right.
The authorized principal can select users. Here we select the user we just created, and select the book resource we just created in the resource type.
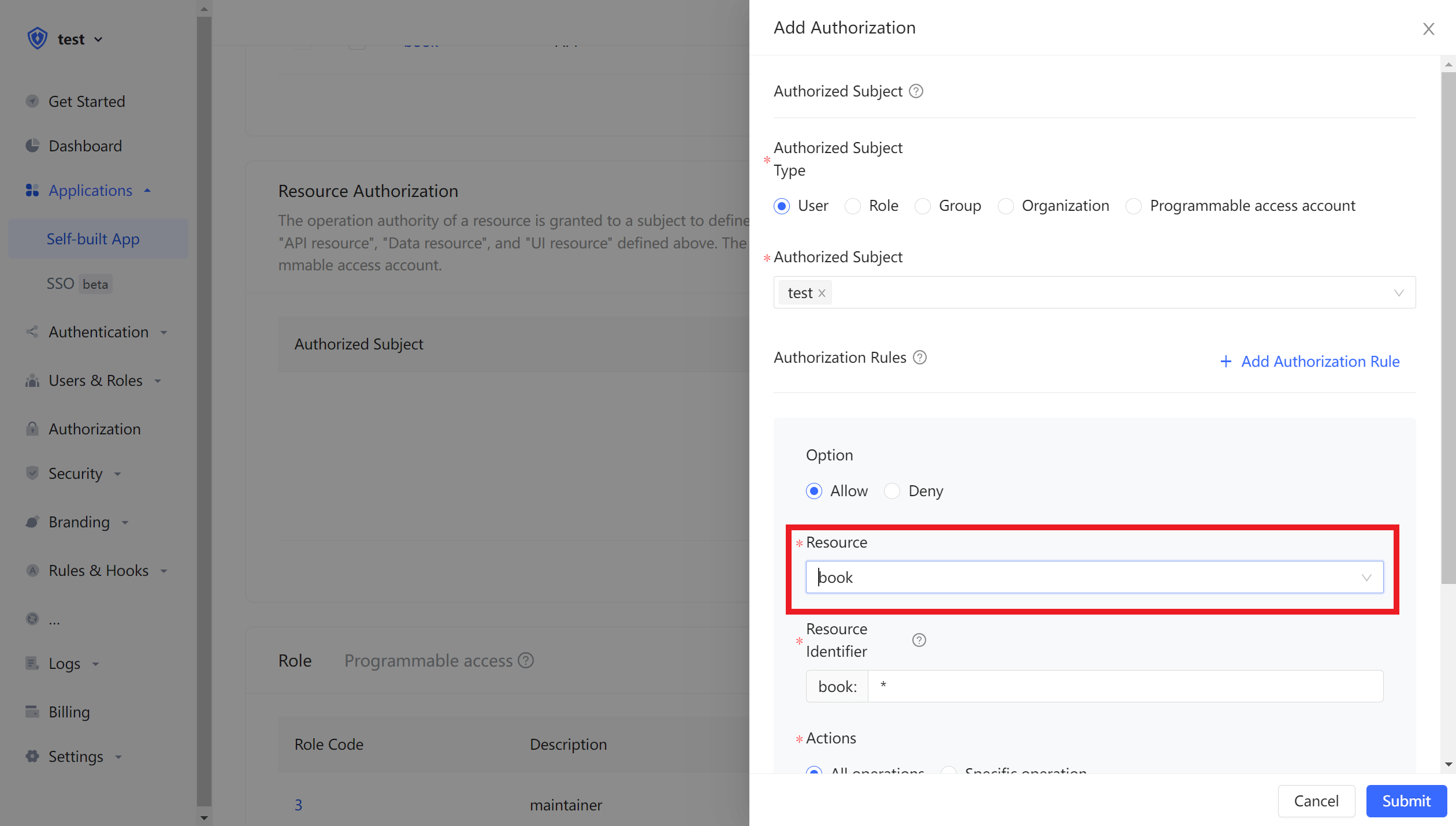
Also, the authorized principal can also choose a role, so that all users in the role will automatically inherit the authorized privileges of the role.
Then fill in the resource id *, which means that all book resources are authorized. Select Specific Operationin Operation, and then select the read book list operation in the Resource Operation we just defined, and finally clicks OK.
If you fill in a specific id, such as 42, it means that the book resource number 42 is authorized to the principal. The principal only has the privilege of the book:42 resource, and can only authorize the relevant privilege of the book:42 resource during authorization.
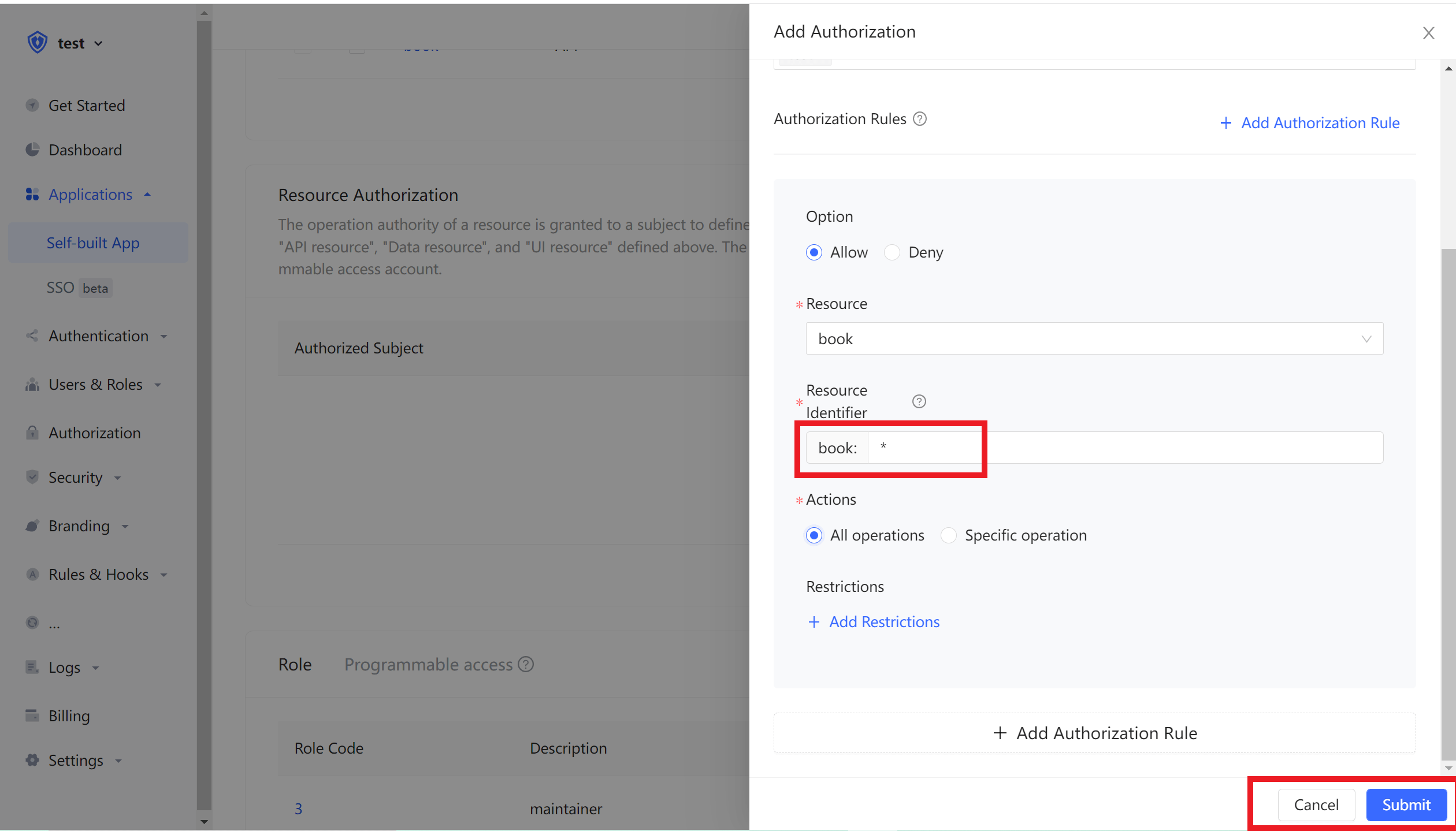
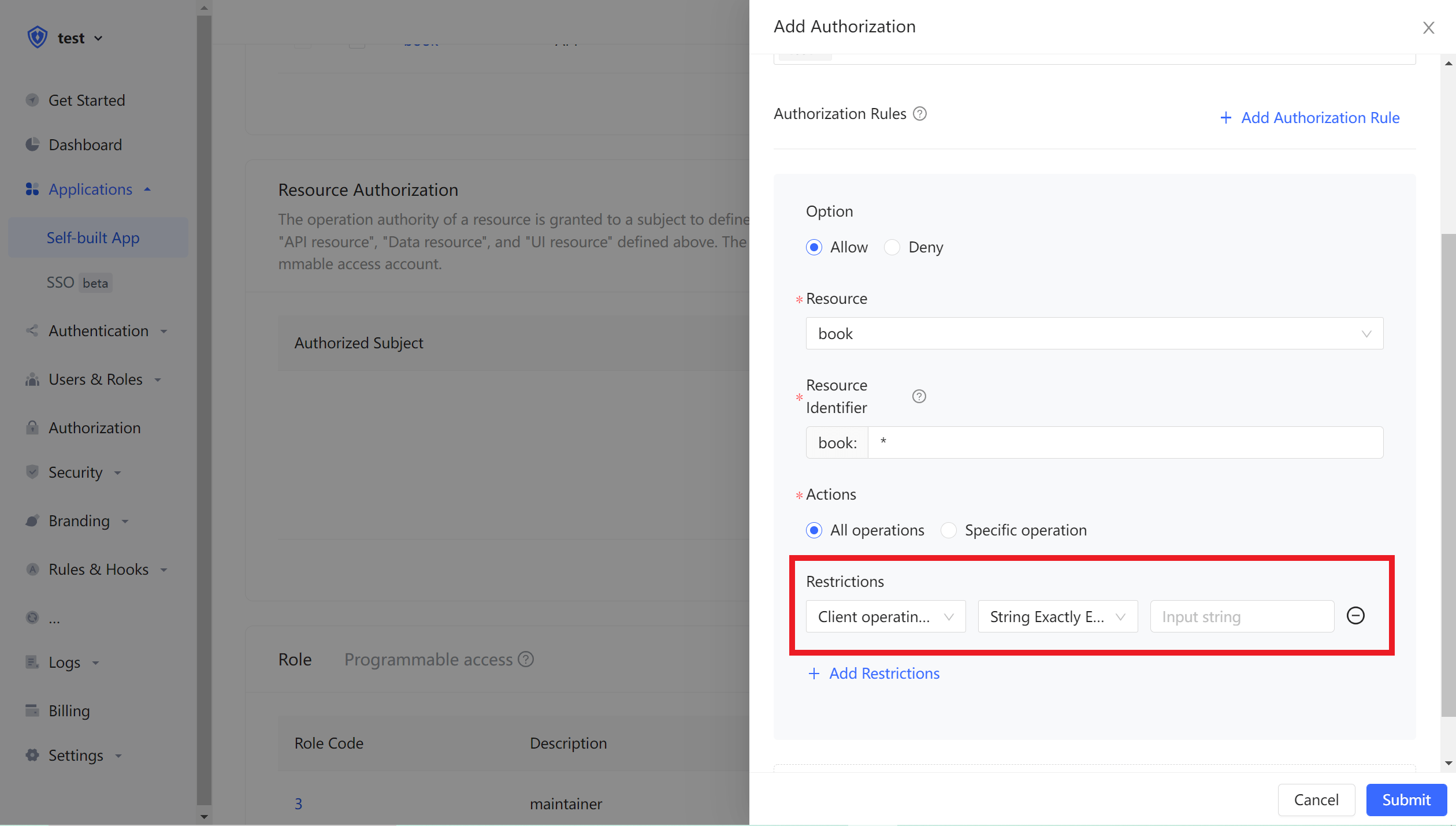
We can also add restrictions to authorization rules. For example, the rules are only valid for Windows users. If the authorization is initiated from a Linux machine, Authing will determine that the user has no permission and cannot complete the authorization of the book resource.
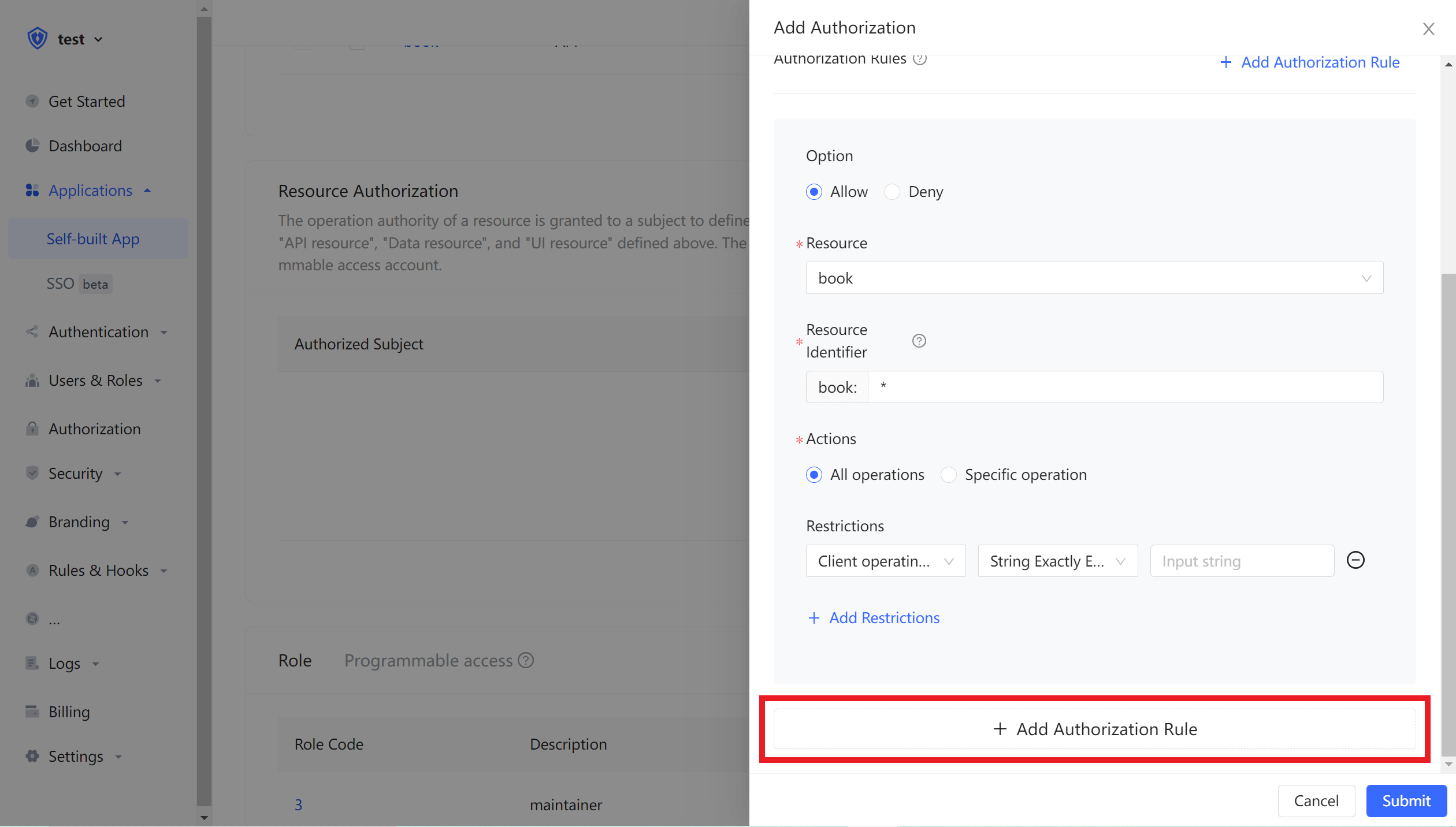
If you want to authorize multiple resources to users, you can continue to add authorization rules.
¶ Programmatic access account
The programmatic access account is a pair of AccessKey and SecretKey in the application, which is used to hand over to third-party vendors. You can use the programmatic access account in combination with the OIDC authorization code to obtain the user's AccessToken and IdToken, or use the programmatic access account to perform OIDC ClientCredentials mode as the caller itself to request authorization.
